Firebird and InterBase codepages
Built-in support of code pages
In IBProvider v3.0.0.6327 new codepages processor was implemented. Support of 49 code pages of Firebird and InterBase is available. Using conversion tables and algorithms the provider converts text columns, BLOB fields and arrays into UCS2 format (two-byte Unicode) with which Firebird and InterBase work. In this case the code page of connection to the database is taken into account.
Along with text code pages IBProvider supports binary data code page — OCTETS.
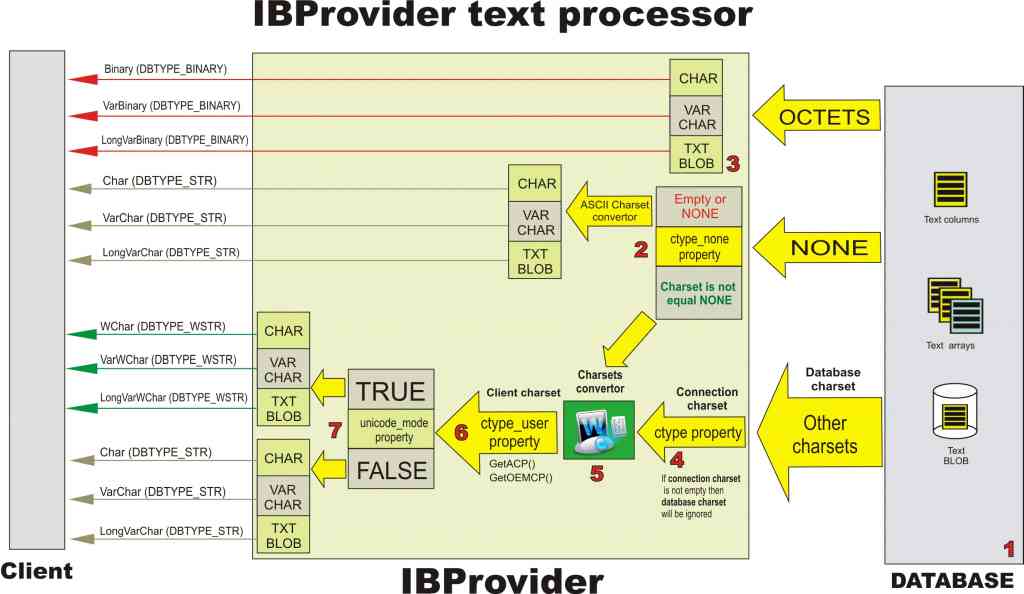
The Figure shows the scheme for working with charsets:
1. Database charset and text column encoding
Set DEFAULT text data charset at database creation. The charset you have chosen will be used for all text data stored in the database. If necessary, you may set the encoding different from the database charset for individual columns, arrays, or BLOB fields.
If text column encoding has been set it will be used, and database charset will be ignored.
2. Charset NONE
If database charset has not been set and text column charset has not been defined, NONE encoding will be used.
IBProvider has ctype_none property for working with this encoding. It allows to set the charset for text data conversion in NONE encoding. If ctype_none property has not been set, ASCII convertor will be used for NONE:
- Codes of characters up to and including 127 will be converted into appropriate characters.
- Codes of characters over 127 will be considered erroneous and exclusion will be generated for them.
Number 2 on the Figure shows the conversion of Firebird and InterBase text data types into appropriate OLE DB and ADO types.
3. OCTETS charset and binary data
OCTETS encoding serves for binary data storage in text columns. When IBProvider detects this charset it will not use encoding processor, OLE DB and ADO data types will be turned into appropriate binary equivalents CHAR, VARCHAR, and BLOB (see number 3 on the Figure).
4-6. Text charsets
Encoding processor is used for charsets different from NONE and OCTETS. See its simplified scheme on the Figure under numbers 4, 5, and 6.
Storage encoding — character set of text column or database charset.
Connection encoding — is defined by ctype initialization property. If it has been set, the data is read and recorded in this encoding and its storage encoding is ignored.
Client encoding — text data charset the client works with. Client encoding is set by ctype_user property. For example, data can be stored in the database in WIN1251 and come to client in UTF-8. When text data is recorded into database it is reversely converted into storage encoding or connection encoding.
If ctype=NONE server ignores connection charset and uses storage encoding.
If ctype_user=NONE provider ignores client charset and represents data to the user in storage encoding or in connection encoding if ctype!=NONE.
ctype_user and ctype properties are ignored for NONE and OCTETS charsets.
Dynamic client encodings (client charsets).
ctype_user permitted values are any charset name supported by the provider and special names of dynamically defined charsets — ACP and OCP.
ACP — provider calls GetACP() and converts ACP into WINDOWS-xxx, where xxx is ANSI system charset identifier.
OCP — provider calls GetOEMCP() and converts OEM into DOS-xxx, where xxx is OEM system charset identifier.
If the provider fails to convert the charset name or it is not supported by the server the provider generates an error.
7. Unicode mode
The provider has unicode_mode property that defines text data publishing format.
If unicode_mode = true then it uses Unicode DBTYPE_WSTR data types: WChar, VarWChar, and LongVarWChar.
If unicode_mode = false then it uses simple DBTYPE_STR types: Char, VarChar, and LongVarChar.
Text columns size in Firebird 2.x
IBProvider started to control text columns size when working with Firebird 2 servers in Unicode mode. If the length of loaded data exceeds the text column size the exclusion will be generated. To avoid column size checking connect in ordinary mode and set Unicode_mode=false.
Aliases of Firebird and InterBase charsets.
IBProvider allows setting the charset by its name, server alias, or by using provider in-built names-aliases. For example, you may define WIN1251 charset by its name WIN1251, by server alias WIN_1251, and through IBProvider aliases WIN-1251 and WINDOWS-1251.
Procession of empty characret set names
Empty values of ctype, ctype_user, and ctype_none properies are changed into NONE.
IBProvider Professional v3 supported character sets
| ID | Charset | Max bytes per Char |
Collation | Language | Aliases |
| 2 | ASCII | 1 | ASCII | English | ASCII7, USASCII |
| 56 | BIG_5 | 2 | BIG_5 | Chinese, Vietnamese, Korean | BIG5, DOS_950, WIN_950 |
| 50 | CYRL | 1 | CYRL | Russian | — |
| 50 | — | — | DB_RUS | Dbase Russian | — |
| 50 | — | — | PDOX_CYRL | Paradox Russian | — |
| 10 | DOS437 | 1 | DOS437 | English—USA | DOS_437 |
| 10 | — | — | DB_DEU437 | DBase German | — |
| 10 | — | — | DB_ESP437 | DBase Spanish | — |
| 10 | — | — | DB_FRA437 | DBase French | — |
| 10 | — | — | DB_FIN437 | DBase Finnish | — |
| 10 | — | — | DB_ITA437 | DBase Italian | — |
| 10 | — | — | DB_NLD437 | DBase Dutch | — |
| 10 | — | — | DB_SVE437 | DBase Swedish | — |
| 10 | — | — | DB_UK437 | DBase English—UK | — |
| 10 | — | — | DB_US437 | DBase English—USA | — |
| 10 | — | — | PDOX_ASCII | Paradox ASCII code page | — |
| 10 | — | — | PDOX_SWEDFIN | Paradox Swedish/Finnish code pages | — |
| 10 | — | — | PDOX_INTL | Paradox International English code page | — |
| 9 | DOS737 | 1 | DOS737 | Greek | DOS_737 |
| 15 | DOS775 | 1 | DOS775 | Baltic | DOS_775 |
| 11 | DOS850 | 1 | DOS850 | Latin I (no Euro symbol) | DOS_850 |
| 11 | — | — | DB_DEU850 | German | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_ESP850 | Spanish | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_FRA850 | French | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_FRC850 | French—Canada | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_ITA850 | Italian | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_NLD850 | Dutch | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_PTB850 | Portuguese—Brazil | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_SVE850 | Swedish | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_UK850 | English—UK | — |
| 11 | — | — | DB_US850 | English—USA | — |
| 45 | DOS852 | 1 | DOS852 | Latin II | DOS_852 |
| 45 | — | — | DB_CSY | DBase Czech | — |
| 45 | — | — | DB_PLK | DBase Polish | — |
| 45 | — | — | DB_SLO | DBase Slovakian | — |
| 45 | — | — | PDOX_PLK | Paradox Polish | — |
| 45 | — | — | PDOX_HUN | Paradox Hungarian | — |
| 45 | — | — | PDOX_SLO | Paradox Slovakian | — |
| 45 | — | — | PDOX_CSY | Paradox Czech | — |
| 46 | DOS857 | 1 | DOS857 | Turkish | DOS_857 |
| 46 | — | — | DB_TRK | DBase Turkish | — |
| 16 | DOS858 | 1 | DOS858 | Latin I + Euro symbol | DOS_858 |
| 13 | DOS860 | 1 | DOS860 | Portuguese | DOS_860 |
| 13 | — | — | DB_PTG860 | DBase Portuguese | — |
| 47 | DOS861 | 1 | DOS861 | Icelandic | DOS_861 |
| 47 | — | — | PDOX_ISL | Paradox Icelandic | — |
| 17 | DOS862 | 1 | DOS862 | Hebrew | DOS_862 |
| 14 | DOS863 | 1 | DOS863 | French—Canada | DOS_863 |
| 14 | — | — | DB_FRC863 | DBase French—Canada | — |
| 18 | DOS864 | 1 | DOS864 | Arabic | DOS_864 |
| 12 | DOS865 | 1 | DOS865 | Nordic | DOS_865 |
| 12 | — | — | DB_DAN865 | DBase Danish | — |
| 12 | — | — | DB_NOR865 | DBase Norwegian | — |
| 12 | — | — | PDOX_NORDAN4 | Paradox Norwegian & Danish | — |
| 48 | DOS866 | 1 | DOS866 | Russian | DOS_866 |
| 49 | DOS869 | 1 | DOS869 | Modern Greek | DOS_869 |
| 6 | EUCJ_0208 | 2 | EUCJ_0208 | EUC Japanese | EUCJ |
| 57 | GB_2312 | 2 | GB_2312 | Simplified Chinese (Hong Kong, PRC) | DOS_936, GB2312, WIN_936 |
| 21 | ISO8859_1 | 1 | ISO8859_1 | Latin 1 | ANSI, ISO88591, LATIN1 |
| 21 | — | — | FR_CA | French—Canada | — |
| 21 | — | — | DA_DA | Danish | — |
| 21 | — | — | DE_DE | German | — |
| 21 | — | — | ES_ES | Spanish | — |
| 21 | — | — | FI_FI | Finnish | — |
| 21 | — | — | FR_FR | French | — |
| 21 | — | — | IS_IS | Icelandic | — |
| 21 | — | — | IT_IT | Italian | — |
| 21 | — | — | NO_NO | Norwegian | — |
| 21 | — | — | DU_NL | Dutch | — |
| 21 | — | — | PT_PT | Portuguese | — |
| 21 | — | — | SV_SV | Swedish | — |
| 21 | — | — | EN_UK | English—UK | — |
| 21 | — | — | EN_US | English—USA | — |
| 22 | ISO8859_2 | 1 | ISO8859_2 |
Latin 2—Central European (Croatian, Czech, Hungarian, Polish, Romanian,Serbian, Slovakian, Slovenian) |
ISO-8859-2, ISO88592, LATIN2 |
| 22 | — | — | CS_CZ | Czech | — |
| 22 | — | — | ISO_HUN | Hungarian | — |
| 23 | ISO8859_3 | 1 | ISO8859_3 | Latin3—Southern European (Maltese, Esperanto) | ISO-8859-3, ISO88593, LATIN3 |
| 34 | ISO8859_4 | 1 | ISO8859_4 |
Latin 4—Northern European (Estonian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Greenlandic, Lappish) |
ISO-8859-4, ISO88594, LATIN4 |
| 35 | ISO8859_5 | 1 | ISO8859_5 | Cyrillic (Russian) | ISO-8859-5, ISO88595 |
| 36 | ISO8859_6 | 1 | ISO8859_6 | Arabic | ISO-8859-6, ISO88596 |
| 37 | ISO8859_7 | 1 | ISO8859_7 | Greek | ISO-8859-7, ISO88597 |
| 38 | ISO8859_8 | 1 | ISO8859_8 | Hebrew | ISO-8859-8, ISO88598 |
| 39 | ISO8859_9 | 1 | ISO8859_9 | Latin 5 | ISO-8859-9, ISO88599, LATIN5 |
| 40 | ISO8859_13 | 1 | ISO8859_13 | Latin 7—Baltic Rim | ISO-8859-13, ISO885913, LATIN7 |
| 44 | KSC_5601 | 2 | KSC_5601 | Korean (Unified Hangeul) | DOS_949, KSC5601, WIN_949 |
| 44 | — | — | KSC_DICTIONARY | Korean—dictionary order collation | — |
| 19 | NEXT | 1 | NEXT | NeXTSTEP encoding | — |
| 19 | — | — | NXT_US | English—USA | — |
| 19 | — | — | NXT_FRA | French | — |
| 19 | — | — | NXT_ITA | Italian | — |
| 19 | — | — | NXT_ESP | Spanish | — |
| 19 | — | — | NXT_DEU | German | — |
| 0 | NONE | 1 | NONE | Codepage-neutral. Uppercasing limited to ASCII codes 97—122 | — |
| 1 | OCTETS | 1 | OCTETS | Binary character | BINARY |
| 5 | SJIS_0208 | 2 | SJIS_0208 | Japanese | SJIS |
| 3 | UNICODE_FSS | 3 | UNICODE_FSS | UNICODE | SQL_TEXT, UTF-8, UTF8, UTF_FSS |
| 51 | WIN1250 | 1 | WIN1250 | ANSI—Central European | WIN_1250 |
| 51 | — | — | PXW_PLK | Polish | — |
| 51 | — | — | PXW_HUN | Hungarian | — |
| 51 | — | — | PXW_CSY | Czech | — |
| 51 | — | — | PXW_HUNDC | Hungarian—dictionary sort | — |
| 51 | — | — | PXW_SLOV | Slovakian | — |
| 52 | WIN1251 | 1 | WIN1251 | ANSI—Cyrillic | WIN_1251 |
| 52 | — | — | WIN1251_UA | Ukrainian | — |
| 52 | — | — | PXW_CYRL | Paradox Cyrillic (Russian) | — |
| 53 | WIN1252 | 1 | WIN1252 | ANSI—Latin I | WIN_1252 |
| 53 | — | — | PXW_SWEDFIN | Swedish & Finnish | — |
| 53 | — | — | PXW_NORDAN4 | Norwegian & Danish | — |
| 53 | — | — | PXW_INTL | English—International | — |
| 53 | — | — | PXW_INTL850 | Paradox Multi-lingual Latin I | — |
| 53 | — | — | PXW_SPAN | Paradox Spanish | — |
| 54 | WIN1253 | 1 | WIN1253 | ANSI Greek | WIN_1253 |
| 54 | — | — | PXW_GREEK | Paradox Greek | — |
| 55 | WIN1254 | 1 | WIN1254 | ANSI Turkish | WIN_1254 |
| 55 | — | — | PXW_TURK | Paradox Turkish | — |
| 58 | WIN1255 | 1 | WIN1255 | ANSI Hebrew | WIN_1255 |
| 59 | WIN1256 | 1 | WIN1256 | ANSI Arabic | WIN_1256 |
| 60 | WIN1257 | 1 | WIN1257 | ANSI Baltic | WIN_1257 | 61 | WIN1258 | 1 | WIN1258 | ANSI Vietnamese | WIN_1258 |
Support of data conversion external libraries
In addition to built-in data conversion tables and algorithms, IBProvider v3 can use external library with text data convertors — ICU. This requires to enter icu_library=icuuc30.dll. parameter in the connect string. The client shall have the library with icuuc30.dll converter algorithms and the resource library icudt30.dll. One can take the libraries from Firebird SQL Server set.
Be careful to use 32-bit ICU-libraries with IBProvider 32bit and 64-bit ICU libraries with IBProvider 64bit. The usage of ICU libraries from Firebird 2.1 set adds the support of GBK and CP943C code pages.
Useful links
Tags: Firebird, InterBase, Firebird codepages, collations, charsets, Firebird encoding, ODBC Firebird driver, UCS2 format, ODBC InterBase driver, character sets, Firebird oledb provider
Supported charsets: ASCII, BIG_5, CYRL, DOS437, DOS737, DOS775, DOS850, DOS852, DOS857, DOS858, DOS860, DOS861, DOS862, DOS863, DOS866, DOS869, EUCJ_0208, GB_2312, ISO8859_1, ISO8859_2, ISO8859_3, ISO8859_4, ISO8859_5, ISO8859_6, ISO8859_7, ISO8859_8, ISO8859_9, ISO8859_13, KOI8R, KOI8U, KSC_5601, NEXT,NONE, SJIS_0208, TIS620, UNICODE_FSS, UTF8, WIN1250, WIN1251, WIN1252, WIN1253, WIN1254, WIN1255, WIN1256, WIN1257, WIN1258, OCTETS, GBK, CP943C